- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2025-09-22 at 2:13 pm #7710
Gene libraries are essential tools in molecular biology and genomics, widely used in gene function research, gene cloning, and drug screening. Conventional gene library construction methods, such as degenerate saturation mutagenesis using NNK or NNS degenerate primers, include 32 (4×4×2) codon combinations corresponding to 20 amino acids. This inevitably leads to codon redundancy, making it impossible to achieve equal-probability amino acid mutations and increasing the risk of introducing stop codons (TAG/TAA), thereby complicating the screening process.
The primer synthesis process used in the Trimer Gene Library differs from that of degenerate primers. Instead of synthesizing degenerate primers, it employs trimers as raw materials, adding three bases per cycle (corresponding to a single amino acid). A Trimer Gene Library contains a maximum of 20 codons, with each codon corresponding to one amino acid.By proportionally mixing Trimer primers, the amino acid composition and ratio can be precisely customized, eliminating the introduction of stop codons and unwanted codons. The actual amino acid distribution closely matches the intended design. Compared to traditional mutagenesis and degenerate synthesis methods, this approach significantly reduces the screening workload, helping to save both time and costs.As a result, the Trimer Gene Library is ideal for creating highly diverse and high-quality libraries.
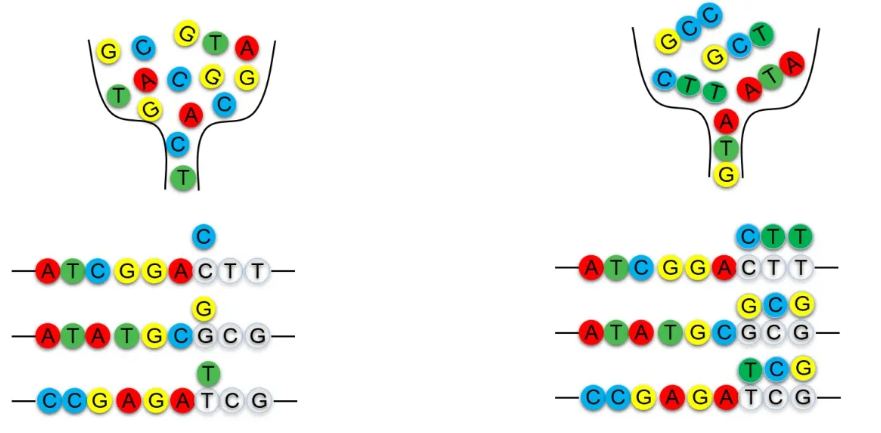
Degenerate Primer Synthesis
Trimer Primer Synthesis
Application Fields
Directed Evolution of Proteins
Protein Engineering: By applying directed evolution to specific proteins, their functionality, stability, and other properties can be enhanced. The Trimer Gene Library enables systematic protein variation, making it possible to screen for variants with desired characteristics.
Exploring Unknown Functions: The Trimer Gene Library allows for diverse protein mutations, facilitating the discovery of proteins with novel biological functions or enzymatic activities, potentially revealing new functionalities.
Drug Resistance Research: By introducing various mutations, the Trimer Gene Library helps study protein changes under drug influence, uncovering mechanisms of pathogen or cancer cell drug resistance, and aiding in the development of new anti-drug strategies.
Antibody Engineering
Affinity Optimization: Enhancing antibody affinity and specificity by designing mutations that improve antigen-binding capability.
Stability Improvement: Increasing antibody stability and tolerance through targeted mutations to extend its half-life in vivo and enhance clinical efficacy.
New Drug Development
Target Discovery: The Trimer Gene Library is used to simulate disease-related amino acid mutations. By generating these variants, researchers can study how mutations affect protein function, uncover disease mechanisms, and identify potential therapeutic targets.
Drug Screening: Custom Trimer Gene Libraries enable drug screening against specific targets, allowing researchers to evaluate the inhibitory effects of different compounds on mutated targets and identify promising drug candidates.
Gene Universal Trimer Gene Library Service
Gene Universal has a professional gene library development team and an advanced technology platform, with extensive experience in Trimer Gene Library construction. We offer one-stop services and customized solutions tailored to your specific needs.
Case Study 1: Equal-Proportion Amino Acid Distribution
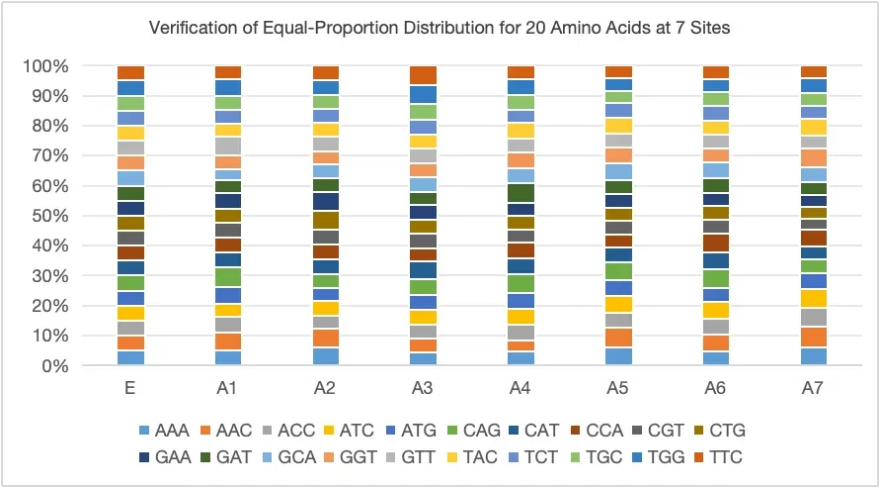
Supports Non-Equal Proportion Customized Mutations, the distribution of various amino acids closely matches the designed proportions.
Case Study 2: Non-Equal Proportion Customized Mutations
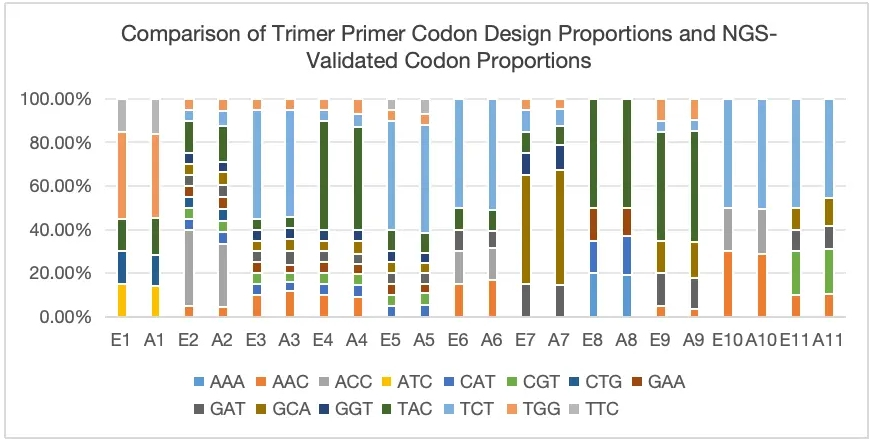
The Trimer Gene Library method enables controlled amino acid distribution, preventing the introduction of stop codons and unwanted amino acids while reducing frameshift mutations. This enhances the precision and accuracy of library screening. With the Trimer Gene Library, high-complexity libraries can be generated with exceptional accuracy. This approach significantly reduces screening workload, saving both time and costs while improving overall efficiency.
Trimer Primer Synthesis Service
Gene Universal offers Trimer Primer Synthesis services, ideal for constructing Trimer libraries and meeting your specific amino acid diversity and preference requirements at targeted sites.
Avoid redundant mutations and stop codons
Design based on amino acid codon mapping, ensuring a one-to-one correspondence between codons and amino acids
Trimer mixed element primer design allows for precise control over the amino acid distribution at mutation sites
Example:
5GCAACTTATTACTGTCAGCAA(X)5-8CYGWTCACGTTCGGACAGGG3
X Trimers=Y(50%)/S (10%)/G(10%)/A(5%)/F(5%)/W(5%)/H(5%)/P(5%)/V(5%)
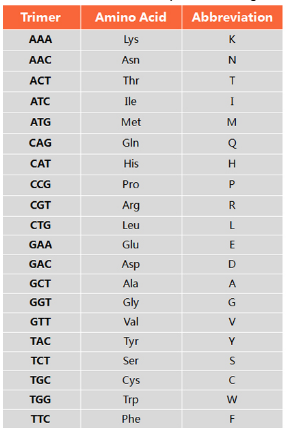
Trimer Codon-Amino Acid Mapping Table
CodonAbbrev
Amino Acid
AAA
K
Lys
AAC
N
Asn
ACC
T
Thr
ATC
I
Ile
ATG
M
Met
CAG
Q
Gln
CAT
H
His
CCA
P
Pro
CGT
R
Arg
CTG
L
Leu
GAA
E
Glu
GAT
D
Asp
GCA
A
Ala
GGT
G
Gly
GTT
V
Val
TAC
Y
Tyr
TCT
S
Ser
TGC
C
Cys
TGG
W
Trp
TTC
F
Phe
Degenerate BasesCodon
Abbrev
Amino Acid
Number
ID
Codon
Abbrev
Amino Acid
Number
ID
R=A/G
TTT
F
Phe
2
1
ATG
M
Met
1
37
Y=C/T
TTC
2
ACT
T
Thr
4
38
M=A/C
TTA
L
Leu
6
3
ACC
39
K=G/T
TTG
4
ACA
40
S=C/G
CTT
5
ACG
41
W=A/T
CTC
6
AAT
N
Asn
2
42
H=A/C/T
CTA
7
AAC
43
B=C/G/T
CTG
8
AAA
K
Lys
2
44
V=A/C/G
TCT
S
Ser
6
9
AAG
45
D=A/G/T
TCC
10
GTT
V
Val
4
46
N=A/C/G/T
TCA
11
GTC
47
TCG
12
GTA
48
AGT
13
GTG
49
AGC
14
GCT
A
Ala
4
50
TAT
Y
Tyr
2
15
GCC
51
TAC
16
GCA
52
TGT
C
Cys
2
17
GCG
53
TGC
18
GAT
D
Asp
2
54
TGG
W
Trp
1
19
GAC
55
CCT
P
Pro
4
20
GAA
E
Glu
2
56
CCC
21
GAG
57
CCA
22
GGT
G
Gly
4
58
CCG
23
GGC
59
CAT
H
His
2
24
GGA
60
CAC
25
GGG
61
CAA
Q
Gln
2
26
TAA
Stop Codon
3
62
CAG
27
TAG
63
CGT
R
Arg
6
28
TGA
64
CGC
29
CGA
30
CGG
31
AGA
32
AGG
33
ATT
I
Ile
34
34
ATC
35
ATA
36
64 Codon Standard Table
References
References 1: Bingrui S ,Xinrui W ,Tianyi Z , et al. Design, Screening, and Characterization of Engineered Phage Endolysins with Extracellular Antibacterial Activity against Gram-Negative Bacteria. [J]. Applied and environmental microbiology, 2023, 89 (7): e0058123-e0058123.
References 2: Sayous V ,Lubrano P ,Li Y , et al. Unbiased libraries in protein directed evolution [J]. BBA – Proteins and Proteomics, 2020, 1868 (2): 140321.
https://www.geneuniversal.com/
Gene Universal -
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.
