- This topic is empty.
-
AuthorPosts
-
2025-06-05 at 6:39 pm #6620
In the field of skin science and cosmetic chemistry, active ingredients are the key to effective skin care formulations. In this blog post, SACH, a high purity skin care raw materials exporter, will share how the active raw material Pro-xylane powder enhances skin activity, including its chemical properties, mechanism of action, etc., and has significant effects in improving skin elasticity, firmness and overall dermal matrix integrity.
Chemical Profile of Active Pro-Xylane Powder
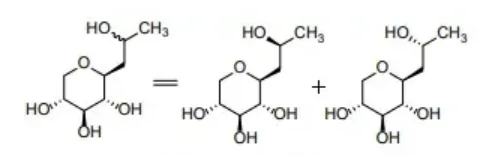
Pro-xylane (CAS No.: 868156-46-1), chemically known as hydroxypropyl tetrahydropyrantriol. Structurally, Pro-xylane is classified as a C-glycoside, a type of molecule where a sugar moiety is linked directly to a carbon atom of another structure, enhancing molecular stability and biological activity compared to traditional O-glycosides.
The stability of the C-glycosidic bond makes Pro-xylane highly resistant to enzymatic degradation, allowing it to persist longer in the skin' s microenvironment and exert sustained bioactivity. Its hydrophilic nature also allows it to interact effectively with water molecules and the skin' s extracellular matrix (ECM), providing a dual action: hydration enhancement and structural reinforcement.
How Active Pro-xylane Enhances Skin Elasticity?
The key to Pro-xylane' s ability to enhance skin elasticity lies in its profound impact on the extracellular matrix (ECM), a complex network of proteins, glycoproteins, and polysaccharides that provide mechanical support and regulate cell behavior.
1. Stimulation of Glycosaminoglycan (GAG) Synthesis
Glycosaminoglycans, such as hyaluronic acid, dermatan sulfate, and heparan sulfate, are critical components of the ECM that maintain skin turgidity, moisture retention, and elasticity. Pro-xylane has been shown to stimulate fibroblasts – the primary ECM-producing cells – to increase the production of GAGs. This effect thickens the ECM, improves its viscoelastic properties, and consequently enhances the skin's resilience and suppleness.
2. Enhancement of Collagen and Elastin Networks
Pro-xylane also influences the deposition and organization of key structural proteins like collagen and elastin. By modulating the expression of genes responsible for collagen synthesis (such as COL1A1 and COL3A1) and elastin assembly, Pro-xylane strengthens the dermal matrix. Clinical observations show an increase in skin density and firmness, with visible improvements in sagging and wrinkling over time.
3. Interaction with Integrins
Integrins are transmembrane receptors that mediate cell-ECM adhesion and signaling. Pro-xylane may indirectly promote integrin-mediated signaling pathways, fostering better anchoring of cells to the ECM and enhancing mechanical tension within the tissue. This biomechanical feedback is crucial for maintaining skin firmness and elasticity.
4. Barrier Function and Hydration
By promoting the production of GAGs and stabilizing the ECM, Pro-xylane also improves the skin's barrier function, minimizing transepidermal water loss (TEWL). Improved hydration levels in the skin contribute to a plumper appearance and a smoother texture, which are closely tied to perceived elasticity.

Clinical Evidence Supporting Pro-xylane' s Efficacy
Numerous in vitro, ex vivo, and clinical studies have substantiated the benefits of Pro-xylane on skin elasticity:
– In vitro studies demonstrate that fibroblasts cultured with Pro-xylane exhibit enhanced GAG production by up to 400% compared to control groups.
– Ex vivo analyses on human skin explants have revealed that Pro-xylane-treated tissues show a notable increase in dermal thickness, improved collagen fiber organization, and enhanced overall biomechanical properties.
– Clinical trials involving topical application of Pro-xylane-containing formulations over periods ranging from 6 to 12 weeks report significant improvements in skin firmness, elasticity, and wrinkle reduction. Skin biomechanical measurements, such as cutometry and elastometry, provide quantitative backing to these subjective improvements.
Formulation Considerations: Optimizing Pro-xylane Delivery
– Concentration: Effective Pro-xylane concentrations in skincare products typically range from 1% to 5%, with 3% being commonly cited in clinical efficacy studies.
– Formulation Stability: Given its hydrophilic nature, Pro-xylane is best formulated in aqueous-based systems or emulsions with controlled pH (around 5.0–6.0) to ensure optimal stability and skin compatibility.
– Synergistic Ingredients: Combining Pro-xylane with other active agents such as hyaluronic acid, Vitamin C (ascorbic acid), peptides, and niacinamide can enhance its performance by addressing multiple aspects of skin aging simultaneously.
– Delivery Systems: Encapsulation techniques such as liposomal delivery or nanocarriers are being explored to improve Pro-xylane penetration into deeper layers of the skin and to prolong its bioavailability.
Advantages Over Other Anti-Aging Ingredients
Compared to other anti-aging actives like retinoids, which may cause irritation and photosensitivity, or peptides, which have varying degrees of efficacy, Pro-xylane stands out for its:
– High Tolerability: Minimal risk of irritation, making it suitable even for sensitive or compromised skin.
– Broad Mechanism of Action: Acting not just on the surface but within the ECM for comprehensive structural rejuvenation.
– Sustained Effects: Because of its molecular stability, Pro-xylane continues to work over prolonged periods after application, making it ideal for long-term skin maintenance.
Conclusion
Through its multifaceted action on the extracellular matrix – boosting glycosaminoglycan production, reinforcing collagen and elastin fibers, improving hydration, and promoting dermal cell-ECM interactions – Pro-xylane delivers visible, measurable improvements in skin firmness and elasticity. As research progresses, Pro-xylane is poised to remain at the forefront of dermocosmetic innovation, offering powerful solutions for maintaining youthful, resilient skin.
-
AuthorPosts
- You must be logged in to reply to this topic.
